Parasitism is an interspecific form of interaction, in which the representative of a type (parasite) exists partially or completely at the expense of a representative of another type (owner). The taxonomic list of parasitic forms that affect a person is extremely extensive
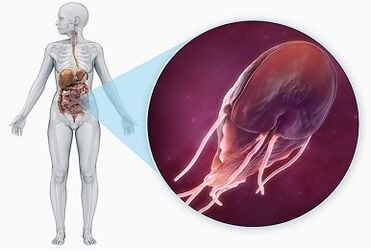
The parasites are among arthropods, mollusks, worms, fungi, simple organisms, and this is not the entire list. Bacteria and route viruses, from a medical point of view, are also parasites.
In this article we will talk about parasitic forms of representatives of the kingdom of property (protozoa). Parasites are always an unpleasant and undesirable phenomenon, therefore, to fight them effectively, you need to know as much as possible about them.
The representatives of the kingdom are often called unicellular organizations. These are creatures that consist of a single cell, which has a constant form, such as ciliates or capable of cytoplasmic movements, such as amoeba.
Many protozoa are equipped with movement organs, represented in the form of flagella, cilia or pseudopods. Its dimensions fluctuate from microscopic to several millimeters. The organism cage contains a set of organelles that performs similar functions to the organs of more complex organisms.
The kingdom is represented by almost 15, 000 species, most of which live in the aquatic and soil environment.
However, there is a part of unicellular organisms that prefer a parasite lifestyle. The simplest parasites of a person can cause a disease such as protozoa, sometimes taking severe forms to death. Sometimes it is very difficult to get rid of the parasite in the body.
Protozoa has a protection mechanism: the transfer of adverse environmental conditions in an inactive state. The cell is covered with a dense and impenetrable layer, becomes cysts, and such non -receptive way can be for a long time. Incest is also used by the simplest to distribute them.
The difference in species
The simplest people of a person differ in structure, the method to introduce them into the body and cause disease. For the best information structuring, the main material on unicellular organisms is briefly presented in the table.
Some representatives of the parasitative protozoa in the human body, their brief description:
- Mania Leish
- Leishmaniosis of skin or pendinskaya ulcer, visceral leishmaniosis or kala random
- Skin, mucous membranes, blood, heart, adrenal glands, kidneys, bone marrow
- Lamblia
- Lambliosis
- The mucous membrane of the small intestine, the gallbladder.
- Trichomonas (intestinal, genitourinary, mouth)
- Trichomoniasis
- The large intestine, the genitourinary system, the oral cavity.
- Tripanosome
- African tripanosomosis or sleepy disease; American tripanosomosis or Chagas disease
- Blood, lymph nodes, spleen, spinal fluid.
- Toxoplasma
- Toxoplasmosis
- Nervous system, eyes, muscles, digestive organs.
- Malaria plasmodium
- Malaria
- Liver, red blood cells.
- Balantidio
- Balantideiosis
- The mucous membrane of the large intestine.
- Amoeba dysentery
- Amebiasis
- The mucous membrane of the large intestine, sometimes, bladder, skin.
As a general rule, for all protozoa, a very complex and multiple life cycle is characterized by a very complex and multiple stages, which includes different in form, degree of activity and functional stages of the stage.
Unicellular organisms occur more frequently through simple cell division in two, but some classes, together with the division, are also inherent in a more complex reproductive process with the exchange of genetic information, for example, representatives of the scourge class.
In addition, protozoa's ways of life are not universal for all classes. Several stages of the life cycle of parasites in organisms of different species of animals can be taken.

Then, some of them are constant owners, carriers of the parasite, while others play the role of an infection bearer. In addition, the individual stages of the life cycle can take place within the same individual, but in different organs.
Invasion symptoms depend on the stage of the parasite life cycle, on the resistance of the human body, the degree of infection and location. Often, the disease is accompanied by non -specific symptoms, as a result of which the diagnosis of infection with protozoa is always extremely difficult.
According to the latest WHO data, more than one billion people are infected with parasites. The worst thing is that parasites are extremely difficult to detect.
- nervousness, weakness, drowsiness;
- frequent headaches;
- itching, allergic reactions;
- Sweat of the mouth, plate on the teeth and language;
- change in body weight;
- diarrhea, constipation and pain in the stomach;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
All these are possible signs of parasites in your body. Parasites are very dangerous, they can lead to fatal diseases. Diseases caused by parasites take a chronic form.


















